#generate incorrect GS1 barcodes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What is a Universal Product Code (UPC)? - Types, Decoding



You've probably seen those barcodes with all the lines and squares on them, but what are they, and what do they do? They are Universal Product Codes. They track products through the supply chain. They're scanned at each point of sale to ensure that the correct product is being sold. It is a barcode symbology widely used in the United States and other countries. It consists of 12 digits that uniquely identify a product. You can find this code on most products that you buy in stores. This blog post discusses the definition, symbology, types, advantages, disadvantages, and requirements of UPC. In addition, the post explains the steps to get UPC for your product.
Definition
A Universal Product Code is a unique code assigned to every item sold in the store. The code helps identify the product, store traffic trends, and inventory details. That helps further in maintaining complete ordering information for the business. It provides real-time data to the store or the supermarket to ensure they never run out of stock for fast-moving items. It also makes the billing system easy and swift. UPC-E (includes zero) and UPC-A (does not have zero) are the two main types of Universal Product Codes.
UPC Symbology

It is made up of four parts: - The number system identifies the type of product; - The manufacturer code, which UCC Council assigns to a specific company; - A unique item identifier or SKU, which is posted by the manufacturer for each product they make; and, - A check digit is calculated using a special algorithm to ensure a valid code. The first digit indicates the product type, and the following five digits are a unique code provided to the vendor. Thus, the vendor will have the same code even if the store differs. The following five digits act as the unique reference specified for the product, and the last digit will be the check digit which is generally used to cross-check if it is correct. It is scanned against a scanner that reads the bar code and lets the system know if everything is okay or not.
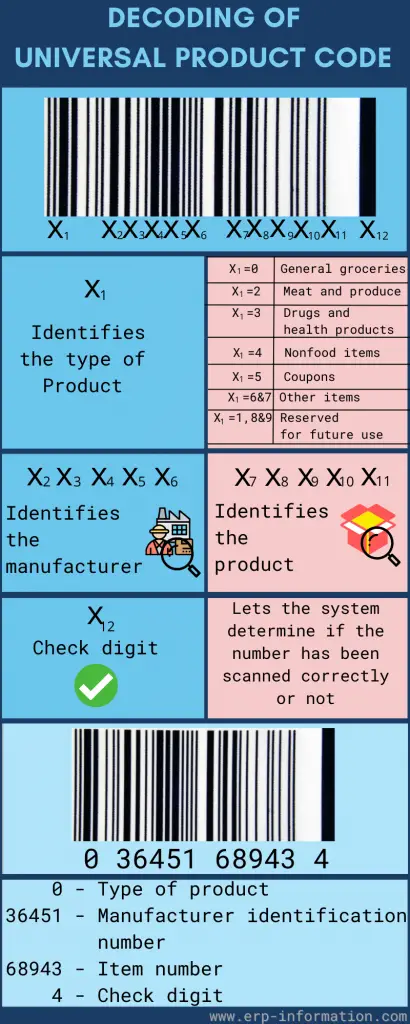
Steps to Get UPC Code for a Product
Application filling The first step is to get the GS1(Global Standard Organization), also known as the Unifor Code Council company prefix. For that, you have to fill out the online application form and sign up for a prefix capacity plan to get it. It shows the number of universal product codes under your company prefix. Paying Fee You have to pay the fee for the code. A prefix capacity plan can be expensive. So make sure that the plan you have chosen will accommodate the long-term use of your business. Once you pay the fee, GS1 allocates a 6-digit number with the manufacturer identification number. This number becomes the first six digits of the universal product code on your company's products. Internal product number generation After getting your company prefix, you can give your product internal product numbers (5 digits). You have the freedom to choose your digits, but each product should have a unique UPC. Ensure that the exact number is not used for more than one product. This 5-digit number represents the product itself. Check digit generation After generating your company prefix and internal product code, generate your check digit. It generates after several calculations by adding and multiplying digits in the code based on an algorithm monitored by the global standard organization(GS1). Manually also, you can calculate the check digit. Confirm check digit is correct or not. If the check digit is incorrect, the UPC code will not scan properly. Registration of final barcode Once all three sets of digits, company prefix, internal product code, and check code are generated, register this number with GS1 so that you will tie your product information to the number you have created. The below infographic provides summarized information on UPC barcode generation steps.

UPC Code's Location
They can be found in most products that you buy in stores. The code is usually located somewhere on the product packaging, and you may also print it on the product. They are also found in product manuals, promotional materials, and shipping boxes.
How to Find a Manufacturer's UPC?
Suppose you want to find the Universal Product Code for a specific product. There are several ways to do so. You can visit the manufacturer's website or contact them directly to ask for the code. You can also use a UPC lookup tool to find the code. These tools are widely available online, and they are free to use. When using a lookup tool, you need the product's name or SKU number. You can usually find the SKU number on the product packaging or manual. Once you have entered the information into the lookup tool, it will return the Universal Product Code for that product. UPC Lookup Tools These tools allow you to search for product codes by keyword or browse by category. They also provide information about the product, such as the manufacturer's name, address, photos, and descriptions. Some tools even let you add products to your inventory. One example is GSOne Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) Database.
Types of UPCs

There are a few different types of Universal Product Codes. The most common type is the 12-digit code used to track store products. Codes can also be 6 or 9 digits long. The 6-digit code is used to track products sold in vending machines, and the 9-digit code is used to track online products.
Universal Product Code Generator
A Universal Product Code Generator is a tool that allows you to create Universal Product Codes for your products. This tool is helpful if you want to make your barcodes for tracking purposes or if you want to include them on your product packaging. There are several generators available online. Most of these tools are free to use and easy to use. You need to enter the information about your product, such as the name and SKU number, and the generator will create a valid code for you.
UPC Barcode Specifications
The Universal Product Code Barcode Specifications are guidelines that describe how they should be formatted and used. These specifications are maintained by the Universal Code Council (UCC), a nonprofit organization that oversees the system. The specifications define the following: - The structure and format - The type of information that can be encoded - How it should be scanned and read - They use it in retail environments - They use it in other industries The UPC barcode Specifications are essential for businesses to create or use barcodes. By following the guidelines in these specifications, companies can ensure that their barcodes will be compatible with scanning equipment and that they will be readable in retail stores.
UPC Code Requirements
To create a barcode, you must encode the product's name or SKU number into a barcode format. There are some free online tools that you can use to do this. Once you have created the barcode, you can print it out and attach it to your packaging. Retail scanners scan and read codes, automatically entering the product information into the store's database. This allows businesses to track their inventory and sales without manually entering the information into their database.
Advantages
- They are easy to use and can be scanned by retail scanners. - They speed up the checkout process in stores. - They help businesses track their inventory and sales. - They can be used to create marketing materials such as flyers and product labels. - They are a global standard and are accepted in most countries.
Disadvantages
- Barcodes can be expensive to create and print. - They are not always accepted in all countries. - They can be challenging to create without using a barcode generator tool. - They may not be suitable for all products or businesses. - They require special scanning equipment to read them correctly.
FAQs
How many types of bar codes are there? There are three types of bar codes. They are 1. Universal Product Code (UPC) 2. International Article Number (IAN) 3. International Standard Book Number (ISBN).What is EANEAN stands for European Article Number, also known as International Article Number. It is an international standard for identifying products and services within the EU and elsewhere. In 2009, 13-digit Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) replaced EAN. EAN-13 is the most commonly used 13-digit EAN standard. What are the differences between UPC and EAN?The differences are as follows. EAN is used mainly in Europe, while UPC is primarily used in the United States. EAN codes have 13 digits, while UPCs have only 12 digits. Furthermore, EANs are encoded to contain information about the product's country or region of origin. In contrast, UPCs do not include this information because they are only used in the US and Canada.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned what Universal Product Codes are and how businesses can use them. You also learned about their advantages and disadvantages of them. We hope the article provided quality information. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
GS1 Barcode Processing & Improved QR Coded Barcode Recognition using Java
What’s new in this release?
Aspose team is pleased to announce the new version of Aspose.BarCode for Java 17.04.0. The major development in this release is the enhanced functionality of GS1 coded barcode. GS1 code format can contain complex elements with digits and letters. Enhanced GS1 barcode functionality now can parse and validate these complex combinations. Improved QR coded barcode recognition functionality has also been incorporated in this release. Aspose.BarCode for Java now generates AI (Application Identifier) compliance GS1 coded barcode. Checksum calculation and validation for many AI specifications have been implemented. As an example, consider code text “(703)123”, this is an incorrect code text (ref: 703 AI, with letters – 324a, with more than 4 symbols). Aspose.BarCode will generates exception if user tries to generate the barcode with EncodeTypes as GS1Code128.Targets detection logic for QR coded barcode has been updated. Aspose.BarCode for Java can now detect QR coded barcode in combination with MaxQuality mode for better accuracy. This release also enhanced Recognition process of QR barcode in MaxBarCodes mode and Functionality of ExportToXml method has been improved. ExportToXml method now export dimension properties along with other properties of the newly define barcode into XML file. Below is the list of main improved features and bug fixes added in this release.
Improve GS1 parsing and validation
Improve targets detection for QR
BarCodeBuilder allows to generate incorrect GS1 barcodes
Unable to recognize the barcode using Aspose.BarCode
Barcode generator accepts incorrect GS1 codetext
BarCodeBuilder.ExportToXml method is not exporting dimensions of the barcode in the XML file
Newly added documentation pages and articles
Some new tips and articles have now been added into Aspose.BarCode for Java documentation that may guide users briefly how to use Aspose.BarCode for performing different tasks like the followings.
Loading Barcode Images
Applying Checksum Validation
Overview: Aspose.BarCode for Java
Aspose.BarCode is a Java based visual component for generation & recognition of 1D & 2D barcodes to support Java, web applications and J2ME platform. It supports 29+ barcode symbologies like MSI, QR, OneCode, Australia Post, Aztec, Code128, Code11, EAN128, Codabar, Postnet, USPS and also supports image output in GIF, PNG, BMP & JPG formats. Other features include barcode size & color settings, rotation angle & caption. You can render barcodes to images, printers, HTTP servlet response & graphical objects too.
More about Aspose.BarCode for Java
Homepage of Aspose.BarCode for Java
Download of Aspose.BarCode for Java
#GS1 Barcode Processing#QR Barcode Processing#generate incorrect GS1 barcodes#Recognition QR barcode in MaxBarCodes#Loading Barcode Images#Java Barcode API
0 notes
Text
How Do Barcodes Work?
How Do Barcodes Work?
Barcodes function by expressing numbers, letters, or special characters with vertical lines that are purposely spaced apart and may be read by a barcode reader device or a smartphone with a suitable barcode scanning app.
QR codes, for example, are square and have more complicated coding that mimics pixel artwork.

To successfully scan a barcode, you'll need a device that can scan the code as well as a system that can understand and read the data.
In a store, for example, a clerk might utilize the business's barcode scanner to generate information on an item, such as its name and price.
The store's scanner is programmed to read a certain barcode format (perhaps a UPC barcode), and it is linked to a product database represented by those barcodes.
If you use that store's barcode scanner on a book's ISBN barcode, you'll almost certainly receive an error.
It’s because the gadget isn't set up to read ISBN barcodes and isn't connected to the correct database to assist it understand any information.
Note: Using the incorrect scanner on a barcode is like dialing someone's phone number using their ZIP code. Each system uses a unique collection of codes and numbers.
See more: https://youtu.be/QsjdQfjEbfQ
What are the numbers on barcodes?
When you understand what the 12 numbers indicate, you can read a barcode manually.
The Global Trade Item Number is the row of numbers seen on a barcode (GTIN).

The first six digits are the GS1 Company Prefix, a unique identity granted to your company by GS1 US, the group that created barcode standards. The prefix is used to identify your firm globally.
The product being offered is identified by the next five numbers. When a product is connected with your GS1 Company Prefix, it is issued a unique number.
A check digit is the last number. This check digit ensures that your GTIN is successfully generated. It is computed from the preceding 11 digits rather than being assigned at random.
See more: https://barcodelive.org/how-to-read-a-barcode
0 notes
Text
Databar Coded Barcode Generation & Enhanced Barcode Detection from BMP Images using Java
What’s new in this release?
Aspose team is pleased to announce the new version of Aspose.BarCode for Java 17.10.0. This release includes enhanced DatabarLimited and DatabarExpandedStacked coded barcode generation process. Furthermore overall performance of the API has also been improved in this release. DatabarLimited barcode generation process has been improved. The functionality has been improved in such a way that it now allows only (01) AI and 0 or 1 symbol in main data. Generation process of DatabarExpandedStacked has been improved. Aspose.BarCode generator now process the the last row as special case. Pharmacode barcode recognition process has been enhanced. It is now working with property Aspose.BarCode.Recognition.AllSupportedTypes. Whereas generation process now calculates correct bar height. Barcode recognition process have been improved to detect barcodes from BMP format image. MacroPdf417 barcode recognition process has been improved.. Below is the list of main improved features and bug fixes added in this release.
Generates incorrect barcode for DatabarLimited
Generation DatabarExpandedStacked isn't correct
Can't recognize Pharmacode with AllSupportedTypes
Can't recognize second barcode (DatabarExpandedStacked)
Aspose.Barcodes 17.06 BarCodeReader does not recognize a barcode types on .gif image format
Aspose.BarCode is unable to detect barcode in BMP format image whereas the same is working if in JPEG format image
Generates incorrect barcode for UPCE
Incorrect default height of Pharmacode
Incorrect recognition type for MacroPdf417 barcode
Newly added documentation pages and articles
Some new tips and articles have now been added into Aspose.BarCode for Java documentation that may guide users briefly how to use Aspose.BarCode for performing different tasks like the followings.
Generate Multiple Barcodes on a Single Image
Generating GS1-128 AI 8102 Coupon Extended Barcode
Overview: Aspose.BarCode for Java
Aspose.BarCode is a Java based visual component for generation & recognition of 1D & 2D barcodes to support Java, web applications and J2ME platform. It supports 29+ barcode symbologies like MSI, QR, OneCode, Australia Post, Aztec, Code128, Code11, EAN128, Codabar, Postnet, USPS and also supports image output in GIF, PNG, BMP & JPG formats. Other features include barcode size & color settings, rotation angle & caption. You can render barcodes to images, printers, HTTP servlet response & graphical objects too.
More about Aspose.BarCode for Java
Homepage of Aspose.BarCode for Java
Download of Aspose.BarCode for Java
Online Documentation for Aspose.BarCode for Java
#Generate Databar coded Barcode#Pharmacode barcode recognition#calculates correct bar height#Barcode recognition process improved#MacroPdf417 barcode recognition#Java Barcode API
0 notes
Text
Postal Barcode Generation with Specific Height & Enhanced Generating EAN14 Barcode using Java
What’s new in this release?
Aspose team is pleased to announce the new version of Aspose.BarCode for Java 17.8.0. Before this release, it was not possible to set the barcode bar’s height while generating Postal barcodes like postnet, AustraliaPost etc. The major development in this release is the support to generate the postal barcode with specified height. Functionality to recognize GS1Code128 coded barcode has also been improved in this release. Previous versions of Aspose.BarCode, it was not possible to set the height of bars of Postal barcodes like Postnet, AustraliaPost, Planet, OneCode and RM4SCC. Aspose.Barcode for .NET 17.8 now allows developers to set the bar height. The said functionality is illustrated in the code sample on blog announcement page. In addition to above, this release also fixes exceptions that were reported by Aspose valued customers, such as Process of GS1Code128 coded barcode recognition has been enhanced. The functionality has been improved in such a way that it now recognize correct type of GS1Code128 coded barcode, Process of generating EAN14 barcode has been improved, Functionality to recognize DatabarStacked coded barcode has been improved and Functionality of yDimension property has been enhanced. It is now working for 2D barcodes e.g. CodablockF. Below is the list of main improved features and bug fixes added in this release.
Ability generate a postal barcode with specified height
Incorrect recognition type for GS1Code128 barcode
Generates incorrect barcode for EAN14
Unable to get the supplement code text from EAN13 coded barcode
Incorrect recognition type for DatabarTruncated barcode
Can't recognize DatabarStacked code
Incorrect recognition type for Code93Standard barcode
yDimension property doesn't work
Aspose.Barcode is not generating correct UPC-E barcode image when using compact framework
UPC-A barcode is not generating correct barcode image when using compact framework
Image has 3 Code39Standard barcodes in it, Aspose.BarCode is recognizing only 1 barcode
EAN13 barcode is not generating correct barcode image when using compact framework
BarCode text alignment is not correct with Compact Framework
Newly added documentation pages and articles
Some new tips and articles have now been added into Aspose.BarCode for Java documentation that may guide users briefly how to use Aspose.BarCode for performing different tasks like the followings.
Generate Multiple Barcodes on a Single Image
Generating GS1-128 AI 8102 Coupon Extended Barcode
Overview: Aspose.BarCode for Java
Aspose.BarCode is a Java based visual component for generation & recognition of 1D & 2D barcodes to support Java, web applications and J2ME platform. It supports 29+ barcode symbologies like MSI, QR, OneCode, Australia Post, Aztec, Code128, Code11, EAN128, Codabar, Postnet, USPS and also supports image output in GIF, PNG, BMP & JPG formats. Other features include barcode size & color settings, rotation angle & caption. You can render barcodes to images, printers, HTTP servlet response & graphical objects too.
More about Aspose.BarCode for Java
Homepage of Aspose.BarCode for Java
Download of Aspose.BarCode for Java
Online Documentation for Aspose.BarCode for Java
#Generate Postal Barcode Specific Height#Recognizing GS1Code128 barcode#generating EAN14 barcode enhanced#working for 2D barcodes#Java Barcode API#GS1Code128 barcode recognition
0 notes
Text
Working with GS1 Barcode & QR Barcode Detection are Enhanced using .NET
What's New in this Release?
The latest version of Aspose.BarCode for .NET 17.4.0 has been released. The major development in this release is the improved functionality of GS1 coded barcode. Many time GS1 code texts contain complex combination of digits and letters. Functionality of the GS1 barcode has been upgraded in such a way that it can parse and validate those complex combinations. Functionality of QR coded barcode recognition has also been improved and incorporated in this release. Aspose.BarCode for .NET allows developers to generate GS1 coded barcode according to AI (Application Identifier) specifications. Checksum calculation and validation for many AI specifications have been implemented. For example, consider code text “(703)123”, which is an incorrect code text (ref: 703 AI, with letters – 324a, with more than 4 symbols). Aspose.BarCode will throw following exception if user tries to generate the barcode with EncodeTypes as GS1Code128. Algorithm to detect QR coded barcode has been improved. Its targets detection logic has been updated. QR coded barcode can now be detected in combination with MaxQuality mode for better accuracy. This month’s release also includes few bug fixes that were reported by Aspose customers in the previous release, such as Recognition process of QR barcode in MaxBarCodes mode and Functionality of ExportToXml method has been improved. ExportToXml method now export dimension properties along with other properties of the newly define barcode into XML file. Below is the list of new and improved features supported in this version.
Improve GS1 parsing and validation
Improve targets detection for QR
BarCodeBuilder allows to generate incorrect GS1 barcodes
Unable to recognize the barcode using Aspose.BarCode
Barcode generator accepts incorrect GS1 codetext
BarCodeBuilder.ExportToXml method is not exporting dimensions of the barcode in the XML file
Overview: Aspose.BarCode for .NET
Aspose.BarCode is a .NET component for generation and recognition of Linear and 2D barcodes on all kinds of .NET applications. It supports WPF with 29+ Barcode symbologies like OneCode, QR, Aztec, MSI, EAN128, EAN14, SSCC18, Code128, Code39, Postnet, MarcoPDF417, Datamatrix, UPCA etc. Other features include barcode insertion in PDF, Word and Excel documents. Also take image output in BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG and WMF formats. You can also control image styles such as background color, bar color etc.
More about Aspose.Report for .NET
Homepage of C# & VB.NET Barcode Component Aspose.BarCode for .NET
Download of Aspose.BarCode for .NET
Online documentation of Aspose.BarCode for .NET
#QR barcode recognition Improved#Improved Working With GS1 Barcode#Enhanced QR Barcode Working#generate GS1 coded barcode#.NET Barcode API#GS1DataMatrix barcode generation
0 notes
Text
Use Enhanced GS1 Barcode Generation & Recognition in SQL Server Reporting Services
What’s new in this release?
We are happy to announce the new release of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services 17.4.0. The major development in this release is the enhanced functionality of GS1 coded barcode. More often it is seem that GS1 code text contains complex combination of digits and letters. With Aspose.BarCode for SSRS 17.4, parsing and validation of those complex combinations is possible. Aspose.BarCode for SSRS allows developers to generate GS1 coded barcode according to AI (Application Identifier) specifications. New validators have been incorporated that can validate text code having only digits and complex AIs (combination of digits & letters). API will throw an exception in case it fails to validate. According to AI specification (ref: 703 AI, with letters – 324a, with more than 4 symbols) code text “(703)123” is incorrect. Aspose.BarCode will throw following exception if user tries to generate the barcode with EncodeTypes as GS1Code128. The following exception message will be displayed for such an incorrect barcode. Functionality of ExportToXml method has been improved. ExportToXml method now export dimension properties along with other properties of the newly define barcode into XML file. Below is the list of new and improved features added in this new release.
Improve GS1 parsing and validation
BarCodeBuilder allows to generate incorrect GS1 barcodes
Barcode generator accepts incorrect GS1 codetext
BarCodeBuilder.ExportToXml method is not exporting dimensions of the barcode in the XML file
Reorganize properties in Properties Window
Overview: Aspose.Report for .NET
Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services is a .NET solution for the rendering of barcode images in SQL Server 2000, 2005 & 2008 Reporting Services. It supports 29+ linear (1D) and 2D barcode symbologies including MacroPdf417, Australia Post, OneCode, Code128, Code39, PDF417, UPCA, Codabar, MSI and QR etc. Also render barcode images on reports in BMP, JPG, PNG and GIF formats. Other features include EAN-128 application identifiers, DPI resolution settings, barcode size and location adjustments.
More about Aspose.Report for .NET
Homepage of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
Download Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
Online documentation of Aspose.BarCode for Reporting Services
#GS1 Barcode Generation#GS1 Barcode Recognition#GS1 coded barcode support#GS1 barcode validation#export dimensions of barcode in XML#SQL Server Reporting Services
0 notes